Our research program is built on five interconnected themes:
1. Deconvolution of Complex GPCR Signaling Pathways
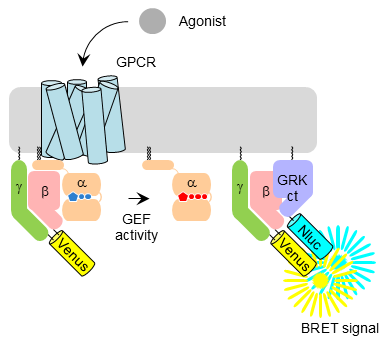
Research question: How do GPCRs achieve signaling specificity across hundreds of receptors and G protein combinations?
Approach: We apply quantitative, live-cell platforms to directly measure GPCR-mediated enzymatic activities across diverse G protein families.
Impact: This work defines fundamental principles of G protein coupling selectivity and signaling bias.
Selected References:
Rules and mechanisms governing G protein coupling selectivity of GPCRs.
Masuho I*, Kise R, Gainza P, Moo EV, Li X, Tany R, Wakasugi-Masuho H, Correia BE, and Martemyanov KA*.
Cell Reports (2023)
*Co-corresponding authorsDiversity of the Gβγ complexes defines spatial and temporal bias of GPCR signaling.
Masuho I, Skamangas NK, Muntean BS, Martemyanov KA.
Cell Systems (2021)
*Co-corresponding authorsA global map of G protein signaling regulation by RGS proteins.
Masuho I, Balaji S, BMuntean BS, Skamangas NK, Chavali S, Tesmer JJG, Babu MM, Martemyanov KA.
Cell (2020)Distinct profiles of functional discrimination among G proteins determine the actions of G protein-coupled receptors.
Masuho I, Ostrovskaya O, Kramer GM, Jones CD, Xie K, Martemyanov KA.
Science Signaling (2015)
2. GPCR signaling in human disease and precision medicine
Research question: How do genetic variants disrupt GPCR signaling and cause disease?
Approach: We combine functional genomics, cellular signaling assays, and structural insights to define pathogenic mechanisms of GPCR- and G protein-associated disorders.
Impact: Our studies establish molecular diagnoses and identify therapeutic opportunities for rare and common diseases.
Selected References:
Gαo is a major determinant of cAMP signaling in the pathophysiology of movement disorders.
Muntean BS, Masuho I, Dao M, Sutton LP, Zucca S, Iwamoto H, Patil DN, Wang D, Birnbaumer L, Blakely RD, Grill B, Martemyanov KA.
Cell Reports (2021)Molecular deconvolution platform to establish disease mechanisms by surveying GPCR signaling.
Masuho I, Chavali S, Muntean BS, Skamangas NK, Simonyan K, Patil DN, Kramer GM, Ozelius L, and Babu MM, Martemyanov KA.
Cell Reports (2018)Pharmacogenomics of GPCR drug targets.
Hauser AS, Chavali S, Masuho I, Jahn LJ, Martemyanov KA, Gloriam DE, Babu MM.
Cell (2018)Novel GNB1 mutations disrupt assembly and function of G protein heterotrimers and cause global developmental delay in humans.
Lohmann K*, Masuho I*, Patil DN, Baumann H, Hebert E, Steinrücke S, Trujillano D, Skamangas NK, Dobricic V, Hüning I, Gillessen-Kaesbach G, Westenberger A, Savic-Pavicevic D, Münchau A, Oprea G, Klein C, Rolfs A, Martemyanov KA.
Human Molecular Genetics (2017)
*These authors contributed equally to this workGNB5 mutation causes a novel neuropsychiatric disorder featuring attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, severely impaired language development and normal cognition.
Shamseldin HE*, Masuho I*, Anazi A, Yamani S, Patil DN, Martemyanov KA, Alkuraya FS.
Genome Biology (2016)
*These authors contributed equally to this workMutations in GNAL cause primary torsion dystonia.
Fuchs T, Saunders-Pullman R, Masuho I, Luciano MS, Raymond D, Factor S, Lang AE, Liang TW, Trosch RM, White S, Ainehsazan E, Hervé D, Sharma N, Ehrlich ME, Martemyanov KA, Bressman SB, Ozelius LJ.
Nature Genetics (2013)
3. Mechanisms of drug action and ligand-directed signaling
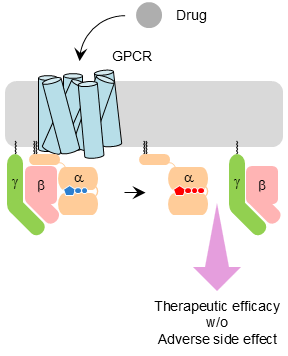
Research question: How do synthetic ligands reshape GPCR signaling pathways?
Approach: We integrate pharmacology, signaling assays, and computational analyses to dissect ligand-directed bias and context-dependent drug responses.
Impact: This work informs rational design of safer and more effective GPCR-targeted therapeutics.
Selected References:
Ligand-directed bias of G protein signaling at the dopamine D2 receptor.
Moo EV, Harpsøe K, Hauser AS, Masuho I, Bräuner-Osborne H, Gloriam DE, Martemyanov KA.
Cell Chemical Biology (2021)Pharmacogenomics of GPCR drug targets.
Hauser AS, Chavali S, Masuho I, Jahn LJ, Martemyanov KA, Gloriam DE, Babu MM.
Cell (2018)Synergistically acting agonists and antagonists of G protein–coupled receptors prevent photoreceptor cell degeneration.
Chen Y, PalczewskaG, Masuho I, Gao S, Jin H, Dong Z, Gieser L, Brooks MJ, Kiser PD, Kern TS, Martemyanov KA, Swaroop A, Palczewski K.
Science Signaling (2016)Distinct profiles of functional discrimination among G proteins determine the actions of G protein-coupled receptors.
Masuho I, Ostrovskaya O, Kramer GM, Jones CD, Xie K, Martemyanov KA.
Science Signaling (2015)
4. Structural principles governing GPCR signaling
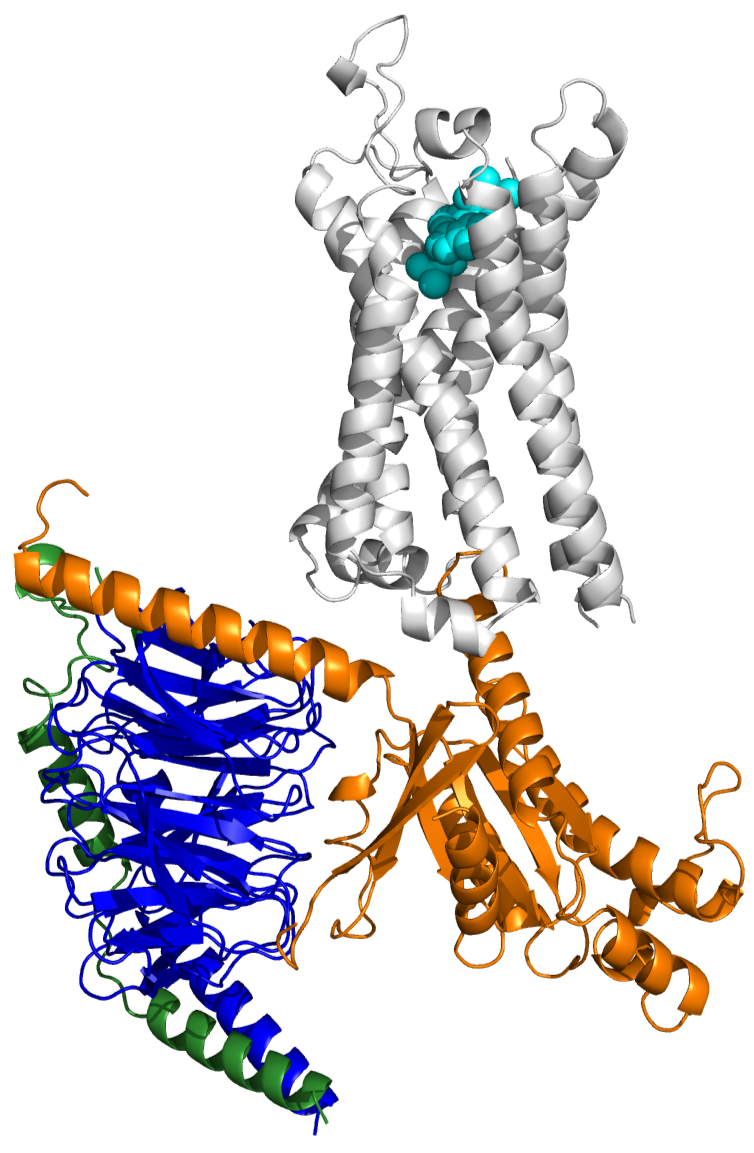
Research question: How does GPCR structure encode signaling specificity and functional diversity?
Approach: Using structural biology, molecular modeling, and functional validation, we investigate how receptor conformations and protein interfaces dictate signaling outcomes.
Impact: This work provides a mechanistic framework linking molecular architecture to signaling behavior and drug action.
Selected References:
The structure and function of the ghrelin receptor coding for drug actions.
Shiimural Y*, Im D, Tany R, Asada H, Kise R, Kurumiya E, Wakasugi-Masuho H, Yasuda S, Matsui K, Kishikawa J, Kato T, Murata T, Kojima M, Iwata S* and Masuho I*
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2025)
*Corresponding authors
5. Evolutionary origins and diversification of GPCR signaling
Research question: How did GPCR signaling systems evolve to support complex physiological functions?
Approach: We combine comparative genomics, evolutionary analysis, and functional characterization across species to understand how conserved architectures give rise to diverse signaling modalities.
Impact: By placing GPCR signaling in an evolutionary context, our research reveals fundamental constraints and opportunities that shape receptor function, disease susceptibility, and pharmacological targeting.
Selected References:
Dopamine receptor DAMB signals via Gq to mediate forgetting in Drosophila.
Himmelreich S*, Masuho I*, Berry JA, MacMullen C, Skamangas NK, Martemyanov KA, Davis RL.
Cell Reports (2017)
*These authors contributed equally to this work